KPNO/CTIO Ohio State Multi-Object Spectrographs (K/COSMOS)
In August 2008, OSU was approached by NOAO (now NOIRLab) to build two new facility spectrographs for the 4m Mayall telescope at Kitt Peak and the 4-m Blanco telescope at CTIO based on the design of OSMOS to provide a modern, high-efficiency spectrograph for the U.S. community that would meet most of the scientific requirements described in the NSF ReSTAR (Renewing Small Telescopes for Astronomical Research) Report.
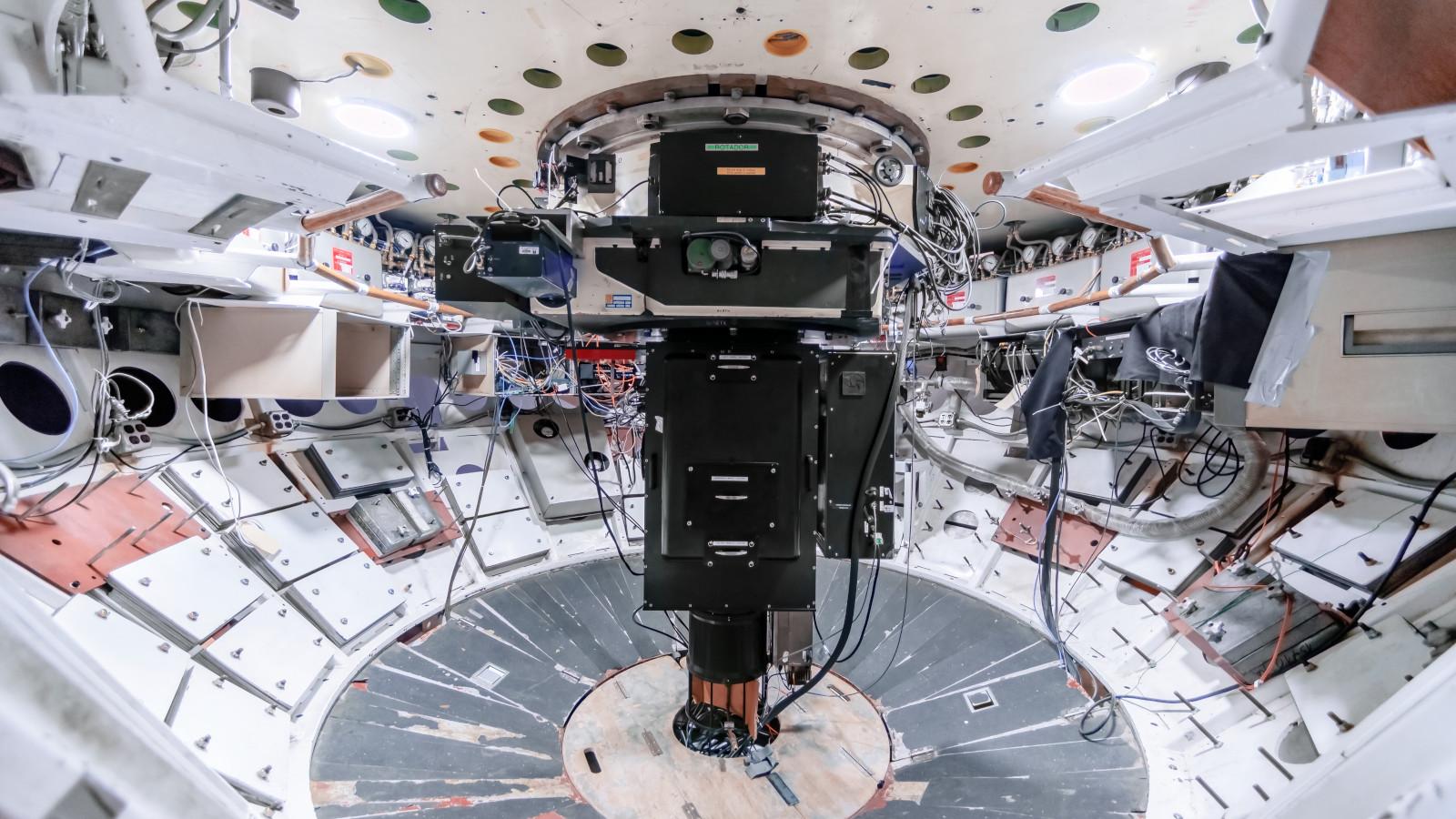
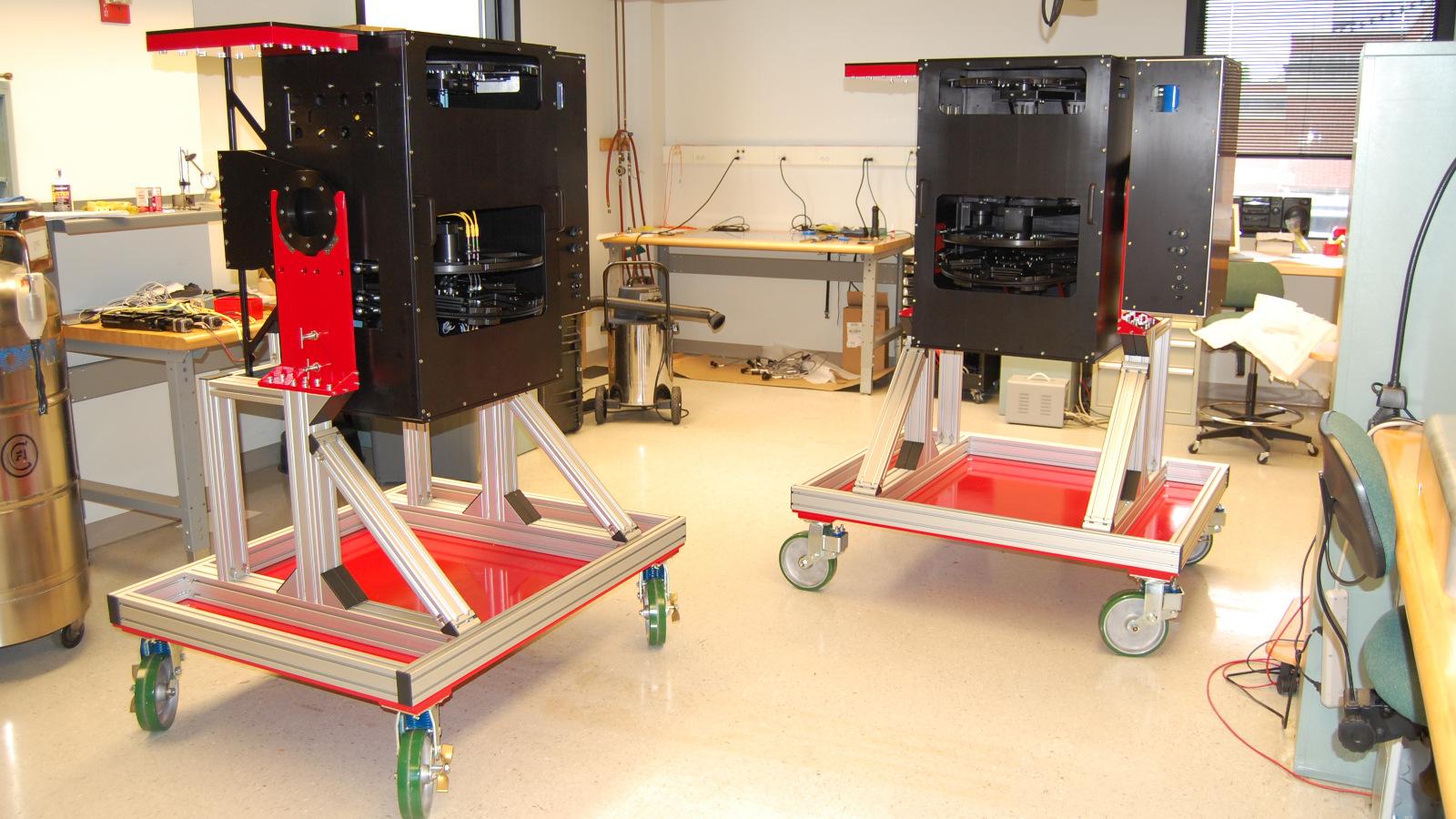
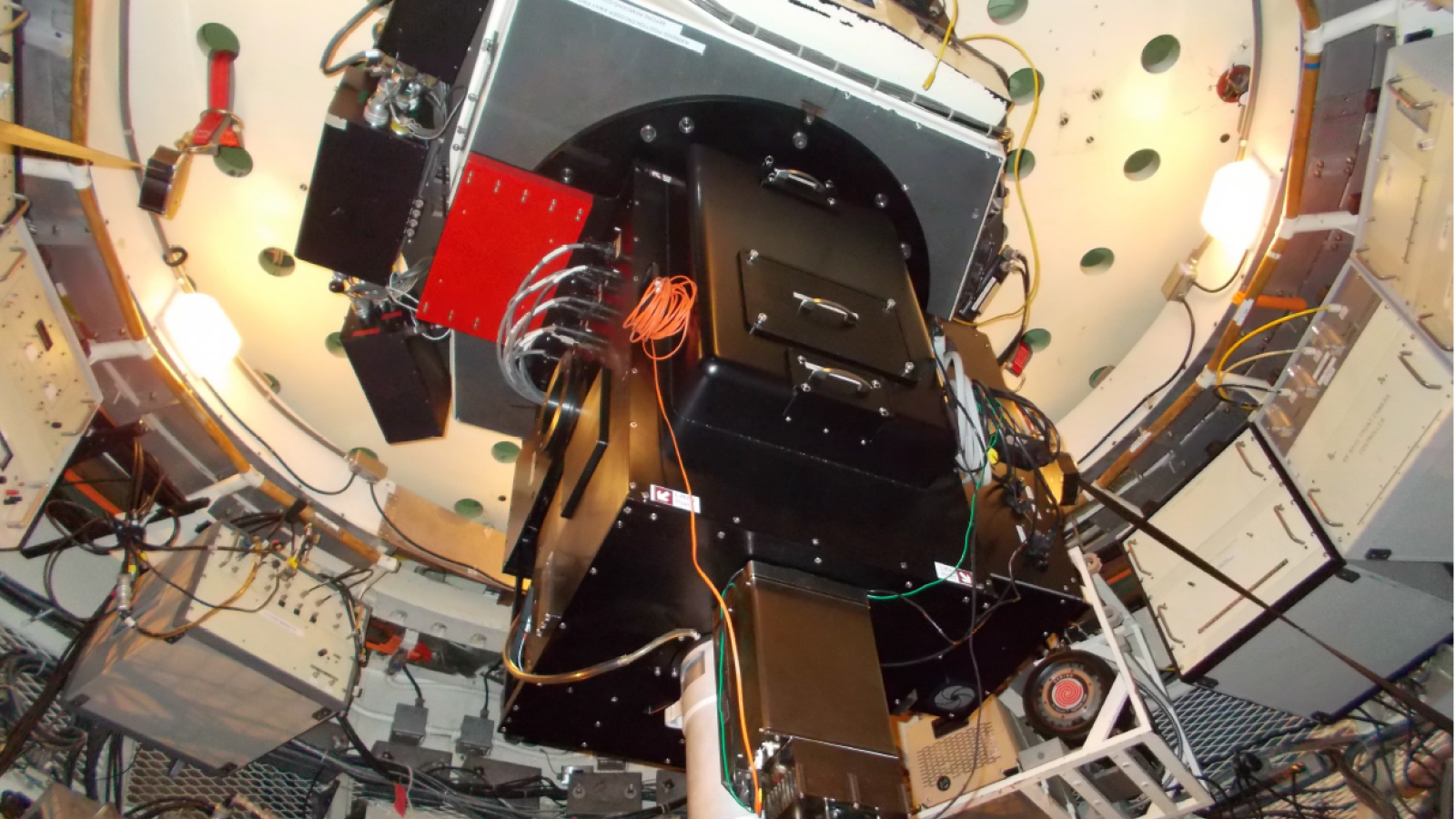
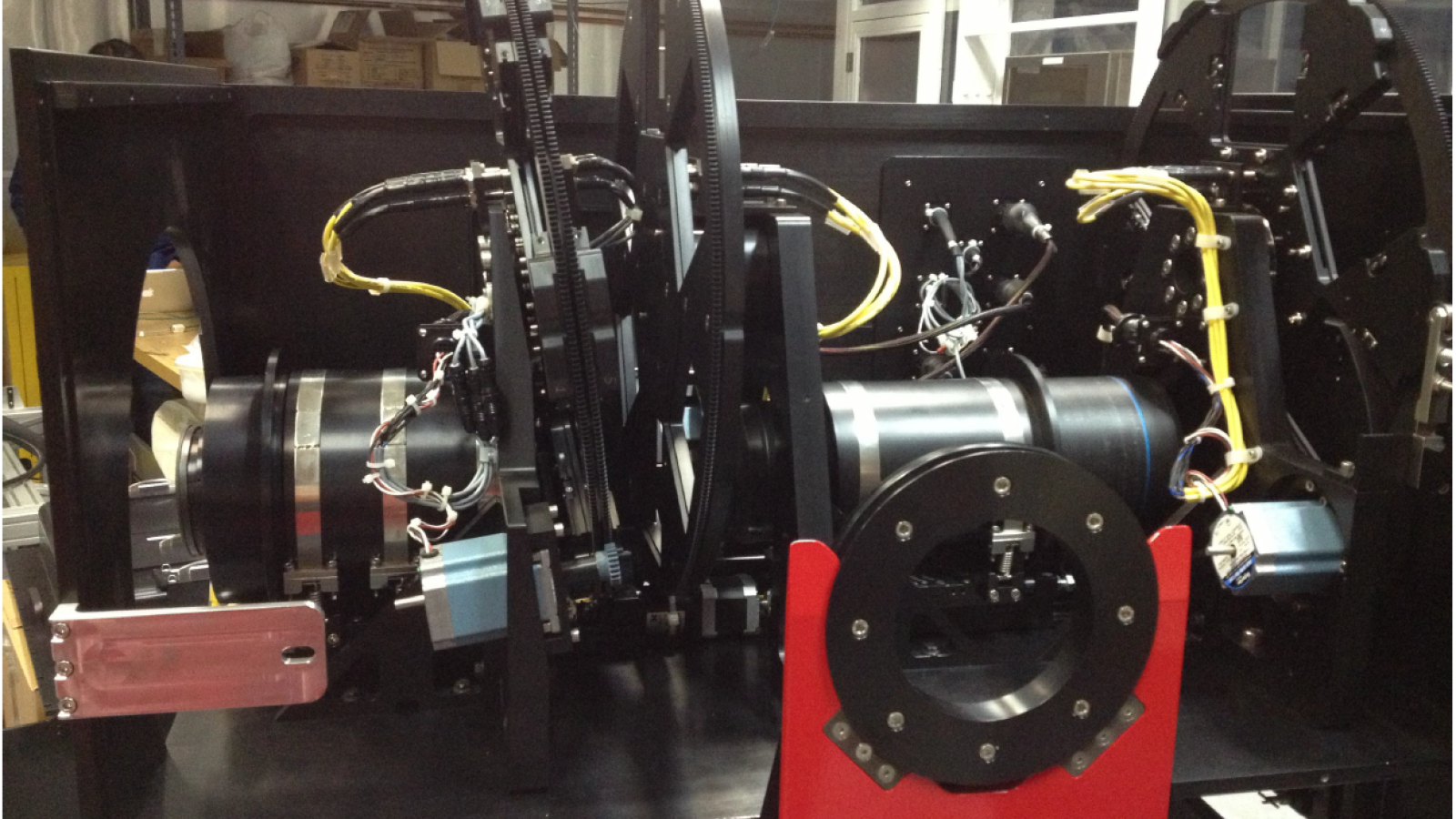
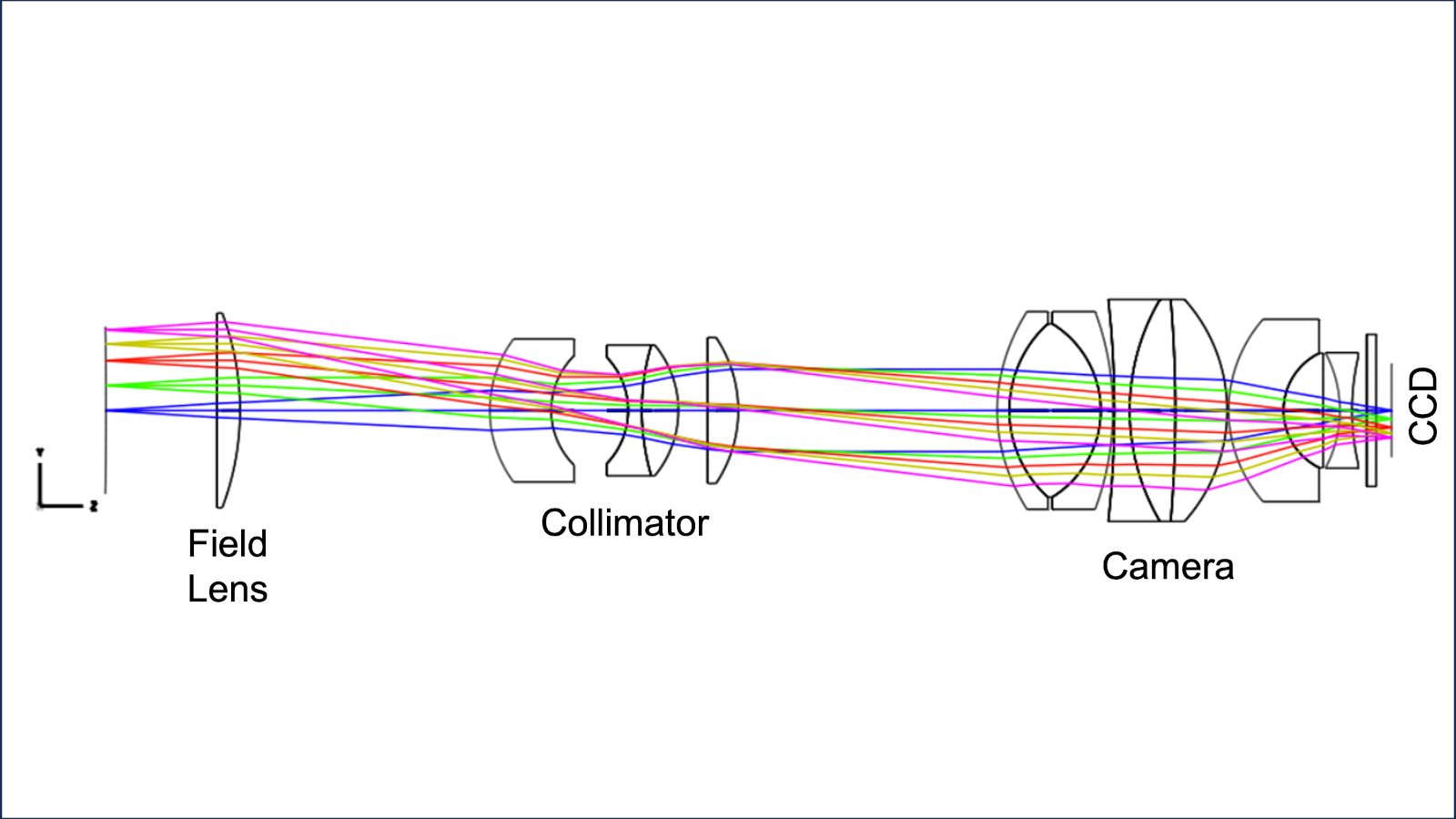
OSU designed a new optical system with oil-coupled lenses to adapt the OSMOS architecture for the 4-m telescopes, built the mechanisms and control systems, and did final assembly and integration. The CCD detector package and data-acquisition software was provided by NOAO. The K/COSMOS spectrographs provide spectral resolutions of 1800-4000 in the 320-980nm range with either long-slits or laser-cut multi-slit masks.
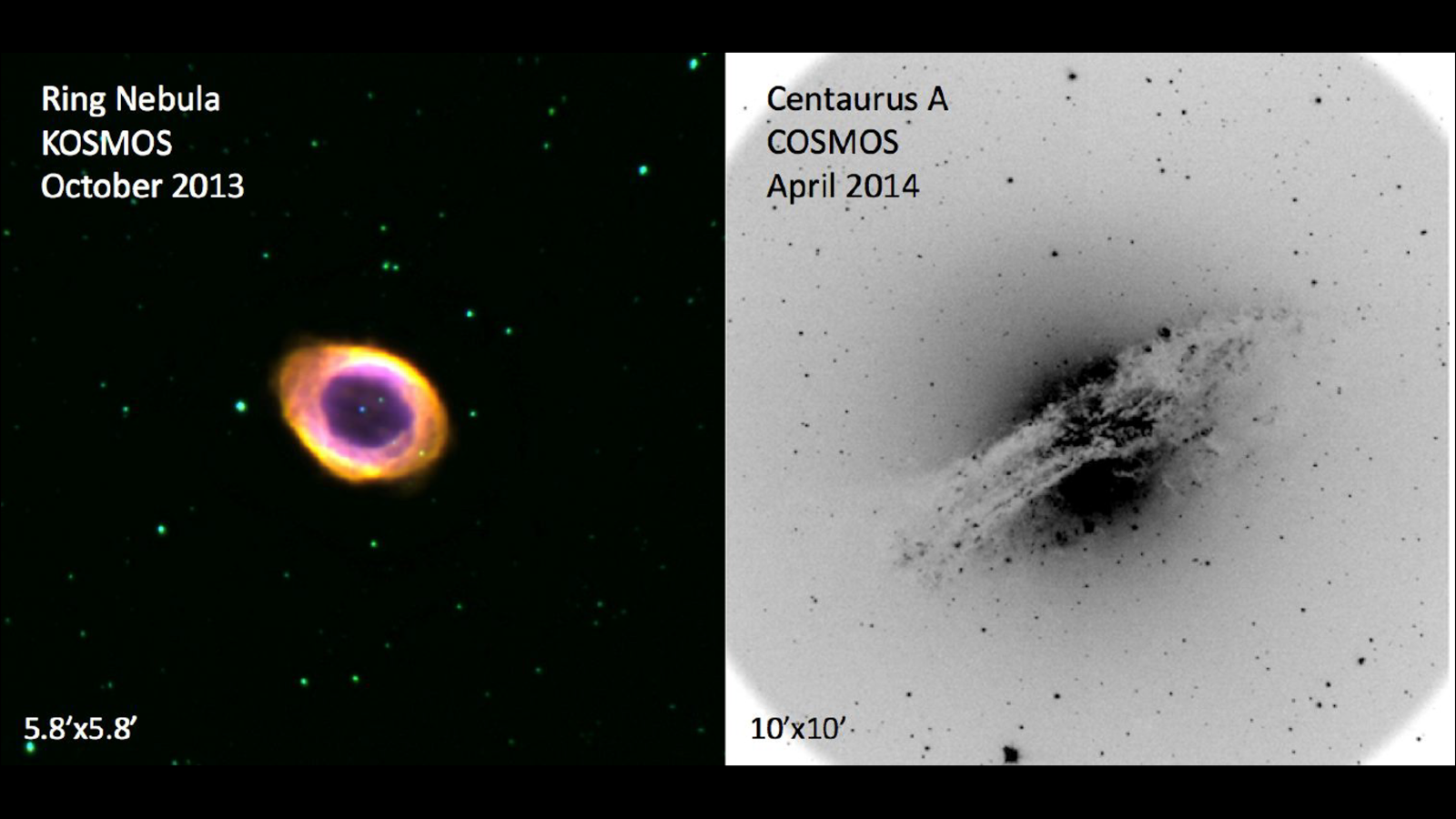
The KOSMOS spectrograph was commissioned on the 4-m Mayall telescope at Kitt Peak in October 2013 where it operated until its retirement in 2018 when the Mayall began to be reconfigured for the DESI project. It was acquired by the University of Washington in 2019 and modified to work on the ARC 3.5m telescope at Apache Point Observatory where it was commissioned in 2021 and began science operations.
The COSMOS spectrograph as commissioned on the 4-m Blanco telescope at CTIO later in September 2014 and continues in operation to the present day.
Instrument Specification
- Project type: Facility Instrument - imager/slit and multi-object spectrometer
- Wavelength: 360-1000nm
- Resolution: R=1800-4000 with VPH gratings
- Field of View: 12-arcminute cropped by the CCD
- Mode/Modes: direct imaging, long-slit, and multi-slit imaging with laser-cut masks
- Primary science: stellar, nebular, galactic, extragalactic, solar system
- Telescopes:
- KOSMOS: KPNO 4m Mayall (2013-2018), ARC 3.5m (2021-present)
- COSMOS: CTIO 4-m Blanco (2014-present)
- Years active: 2013-present
- References: Martini et al. 2014, SPIE, 9147, 0E
Instrument Facts
- Copies of the OSMOS spectrograph at MDM with updated optics and detector systems.
- The oil-coupled lenses in K/COSMOS used a lens cell design derived from one developed for OSU's Imaging Fabry-Perot Spectrograph in the 1990s
- Uses the same mask material (Nicolloy) and laser-cutting technology as the MODS and OSMOS spectrographs.
- K/COSMOS have higher resolutions than the OSMOS spectrograph due to an investment in VPH gratings by NOAO.
- KOSMOS was decommissioned in 2018 to make way for DESI at the Mayall, but was acquired by Sarah Tuttle's group at University of Washington who adapted it to go on the ARC 3.5m telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico where it has been since 2021.
Instrument Team
Paul Martini (OSU PI)/user/931
Jay Elias (NOAO PI)
Mark Derwent (Lead Mechanical Engineer)
Tom O'Brien (Mechanical Engineer)
Ross Zhelem (OSU optics lead)
Greg Poczulp (NOAO optics lead)
Daniel Pappalardo (Electrical Engineer)
Ray Gonzalez (Software Developer/Engineer)
Jerry Mason (Software Systems Developers/Engineer)
Richard Pogge (ISL lead)
Rebecca Stoll (Graduate student)
Dave Brewer (Senior Instrument Maker)
Dave Steinbrecher (Senior Instrument Maker)
Sean Points (CTIO lead)
Rob Seaman (NOAO software lead)