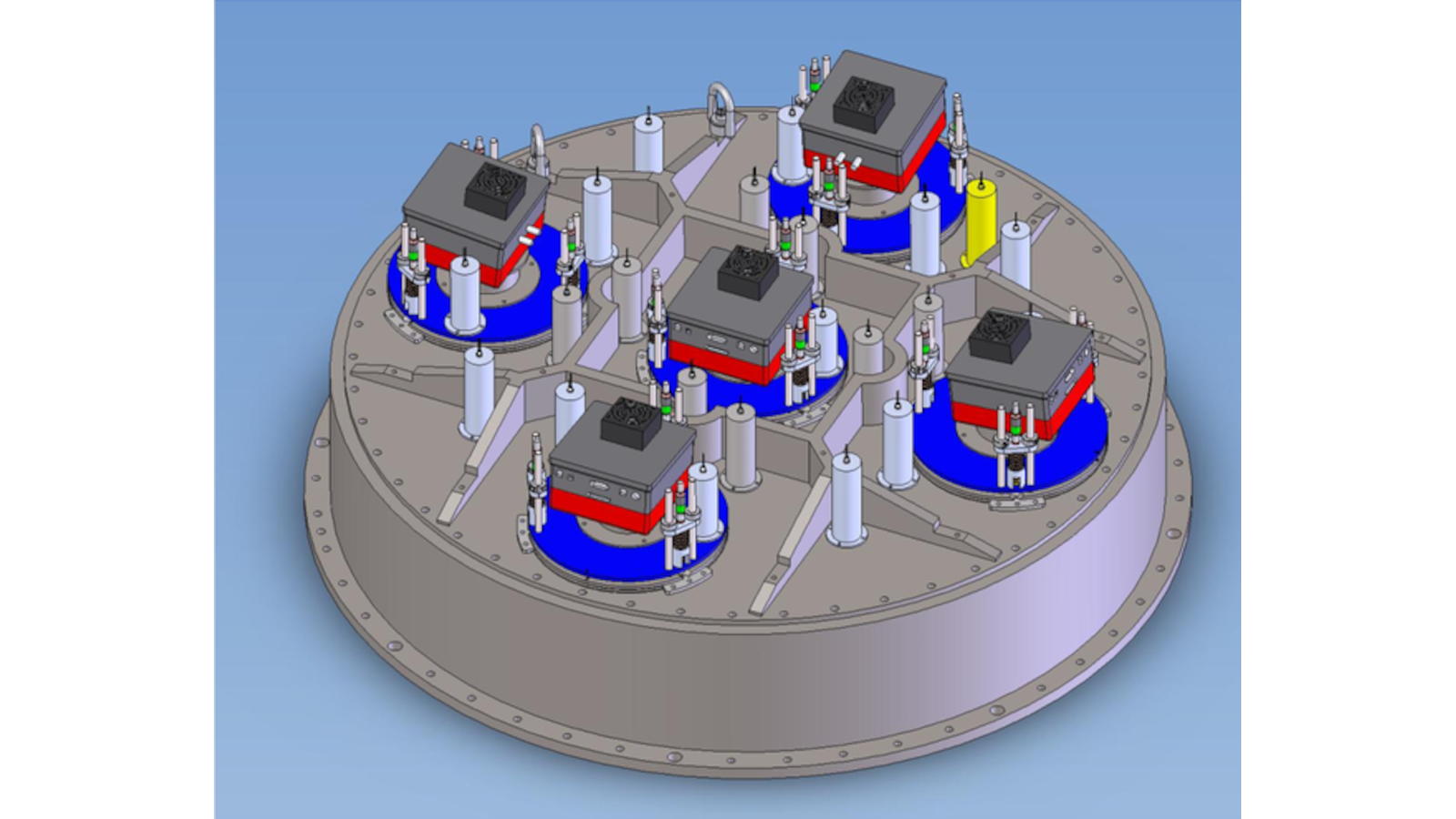
DESI Commissioning Instrument
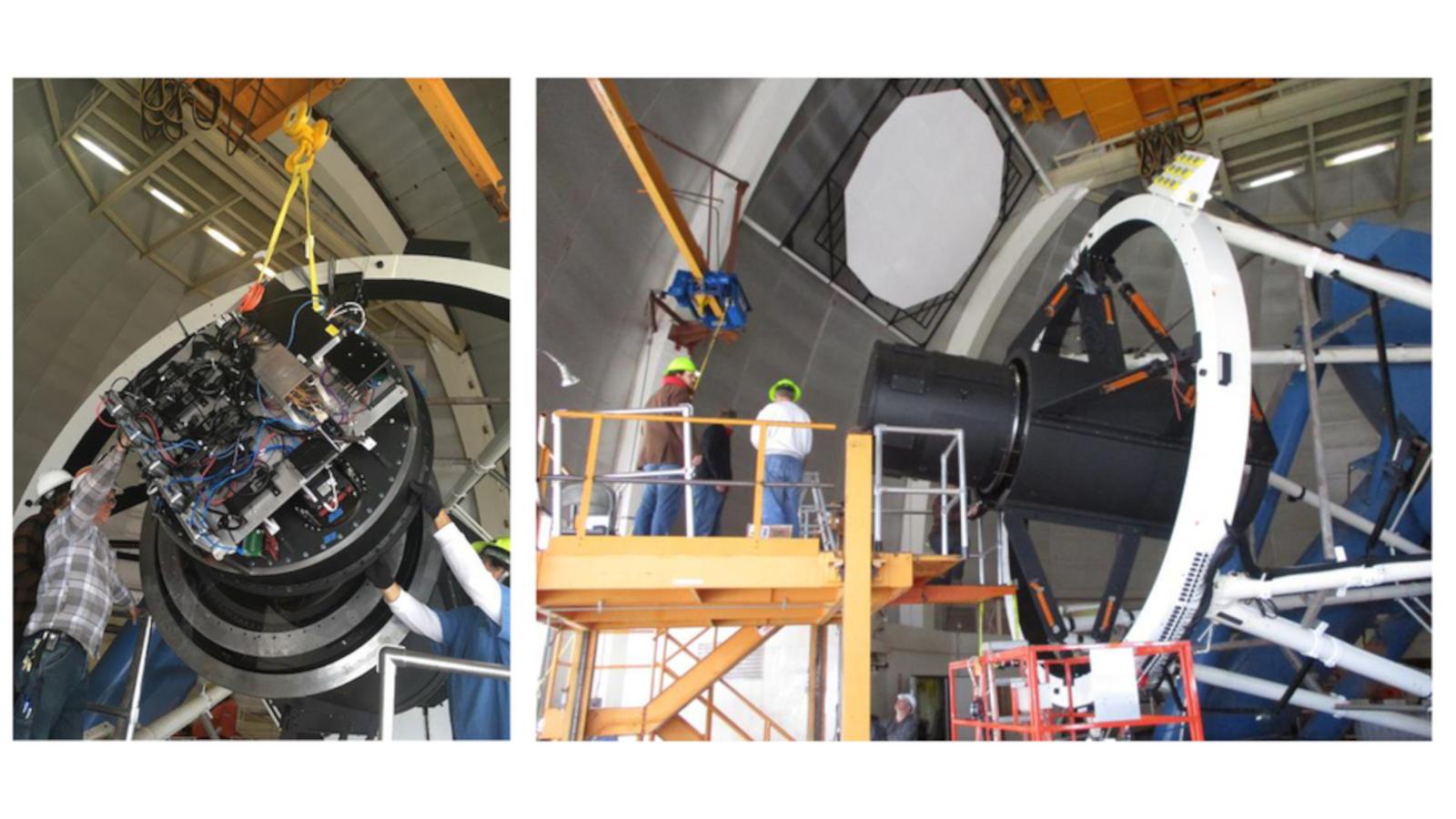
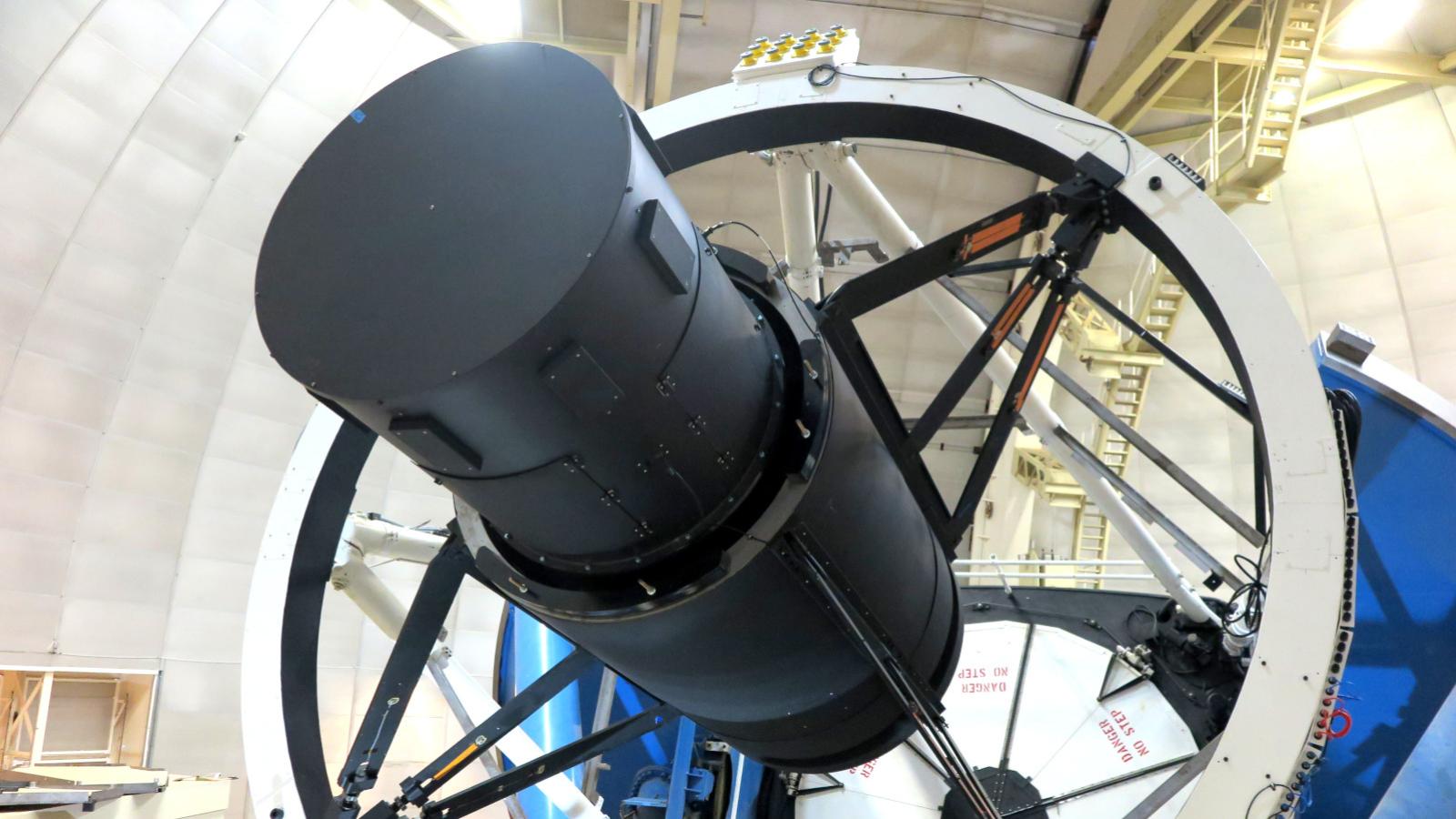
The DESI survey requires excellent imaging quality across a 3-degree field of view on the 4m Mayall telescope at Kitt Peak. To achieve this a new prime focus corrector was installed on the Mayall. The DESI Commissioning Instrument was designed and built by OSU to characterize the image quality of the new corrector and commission key components of the DESI metrology system prior to the installation of the 5000-fiber position DESI Focal Plane System.
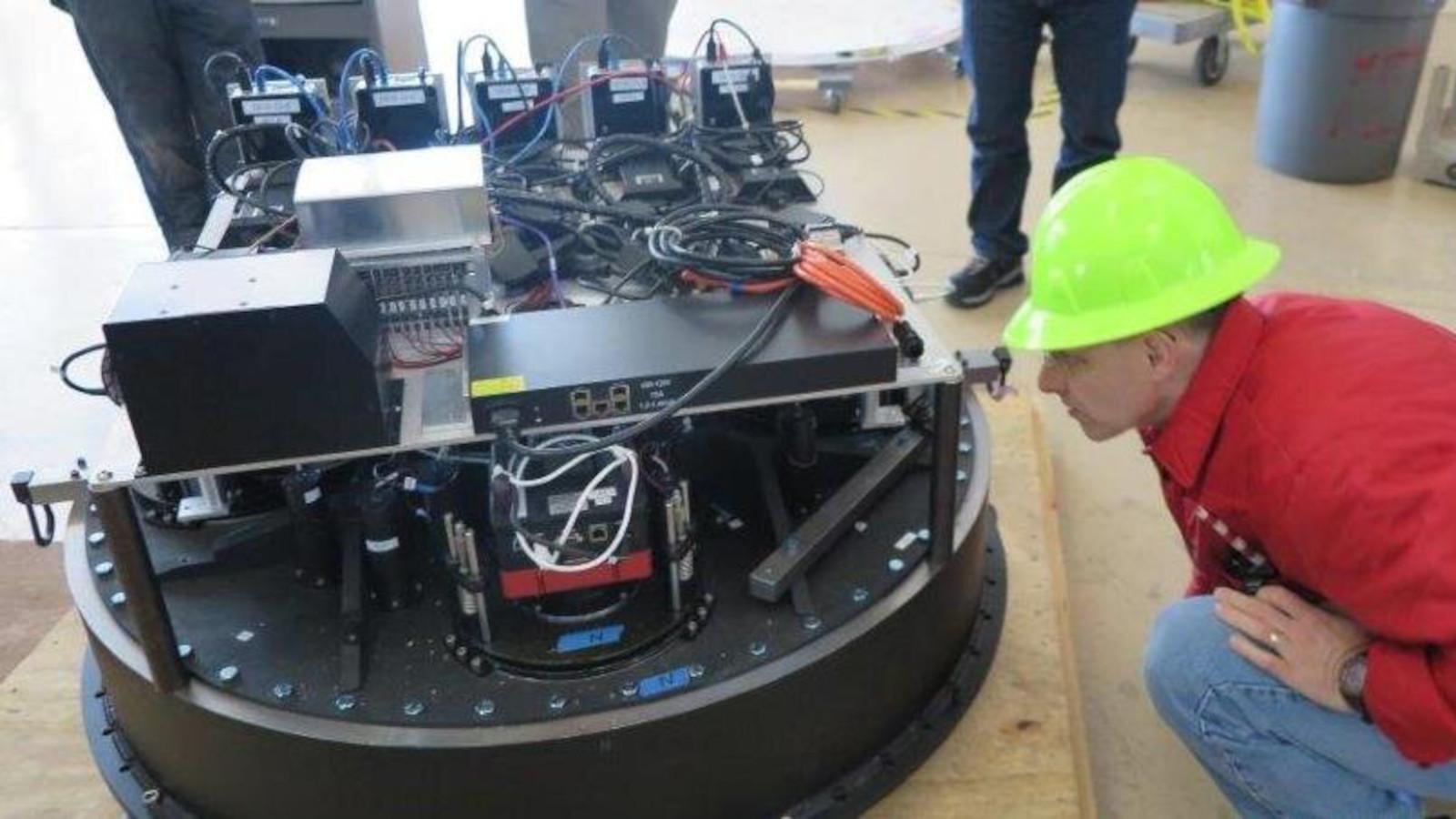
The Commissioning Instrument uses five (5) commercial CCD cameras; one at the center of the focal surface and four located around the periphery of the field at the cardinal directions. A set of 22 illuminated fiducials (the same type using on the DESI focal plane system) are distributed throughout the focal surface to test the fiber viewing camera system and software that is used to map between the DESI fiber positioners and celestial coordinates.
The Commissioning Instrument was installed on the 4m Mayall telescope in March 2019 and undertook a number of basic but important tasks required to bring DESI online: testing the new telescope control system (TCS), telescope guiding, the image optimization system, and DESI’s "Platemaker" algorithm that maps between sky and fiber-positioner coordinates. It was removed in fall of 2019 to make way for installation of the 5000-fiber focal plane system.
Instrument Specification
- Project type: Technical instrument
- CCD Cameras: SBIG STXL-6303e 3Kx2K (5)
- Field of View: 6.6x4.4 arcmin (each)
- Filter: SDSS r
- Additional Systems: 22 illuminated fiducials
- Telescope: Kitt Peak National Observatory 4m Mayall telescope, AZ, USA
- Years active: 2019 March - September
- References: Ross et al. 2018, SPIE, 10702, 80R; Coles et al. 2018, SPIE, 10706, 1LC
Instrument Facts
- Two of the SBIG CCD cameras in the CI were repurposed after it was retired for the DESI Sky Continuum Monitor Instrument.
- The CI discovered an important error in the assumed optical prescription of the Mayall telescope that allowed critical repositioning of the DESI corrector lens before arrival of the fiber positioner system.
- The enclosure of the CI was designed to match the mass and moment of the much heavier 5000-fiber focal plane system to ensure telescope behavior was the same for the CI and the eventual DESI FPS.
- The CI marked the first time the ISL used embedded NUC computers running Linux that were to become the workhorse embedded systems for the DESI spectrograph controllers and the SDSS-V Focal Plane Systems.
Instrument Team
Ashley Ross (Project Lead)
Paul Martini (DESI project scientist)
Rebecca Coles (OSU postdoc - metrology lead)
Mark Derwent (lead mechanical engineer)
Tom O'Brien (mechanical engineer)
Daniel Pappalardo (electrical engineer)
Jon Shover (Senior Instrument Maker)
Suk Sien Tie (OSU graduate student)
Klaus Honscheid (Software systems lead)