Korean Microlensing Telescope Network Cameras (KMTCam)
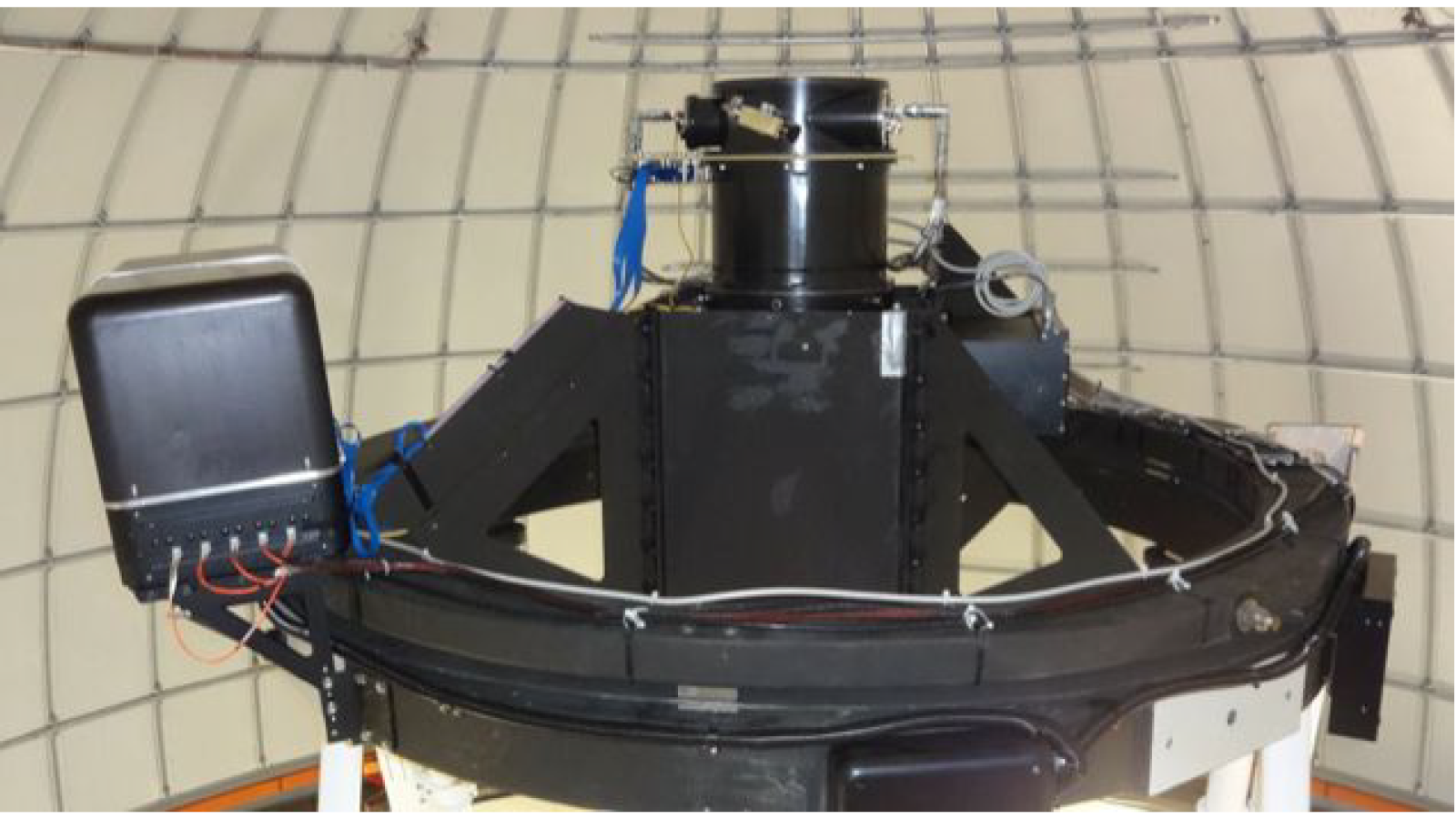
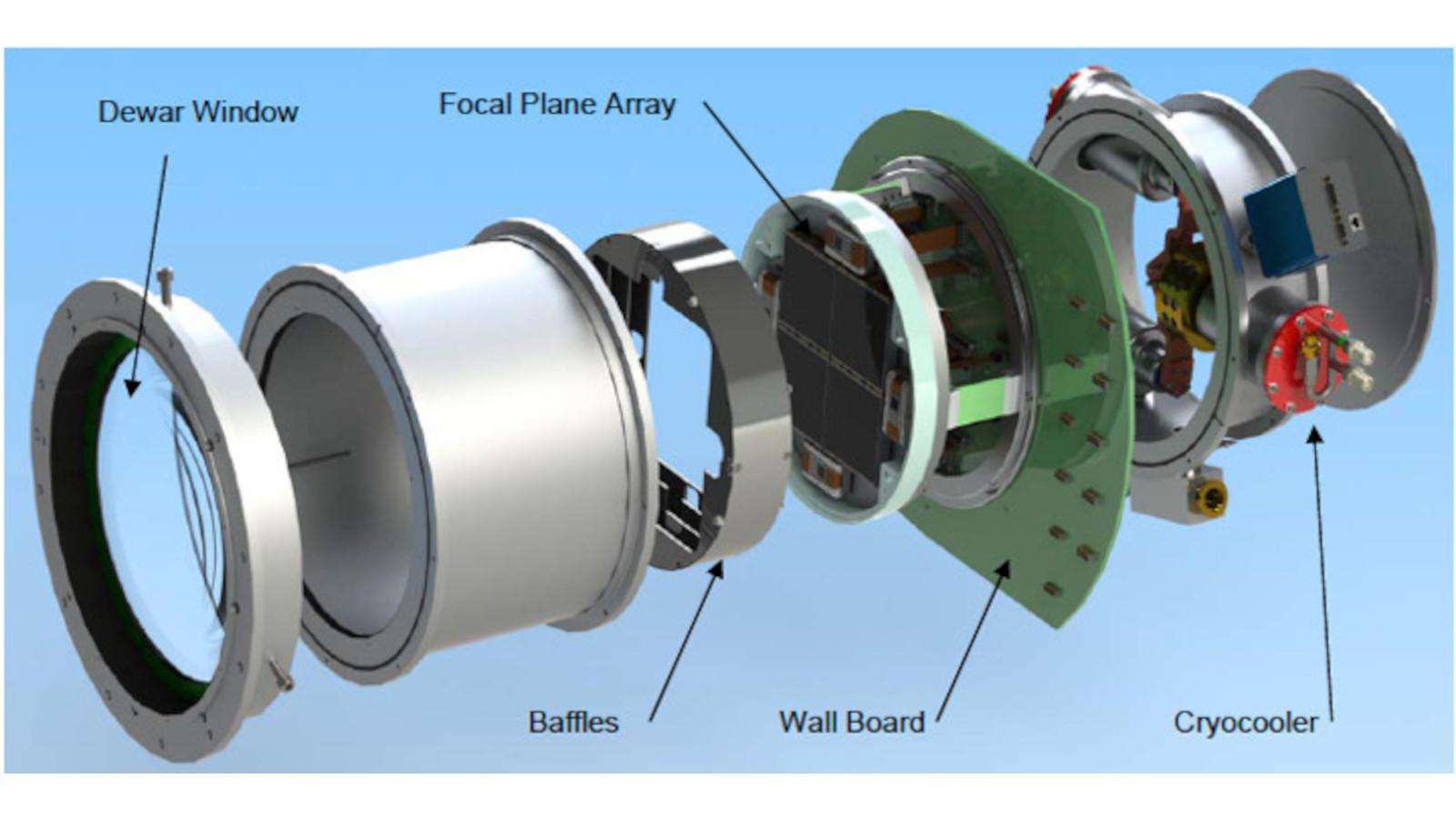
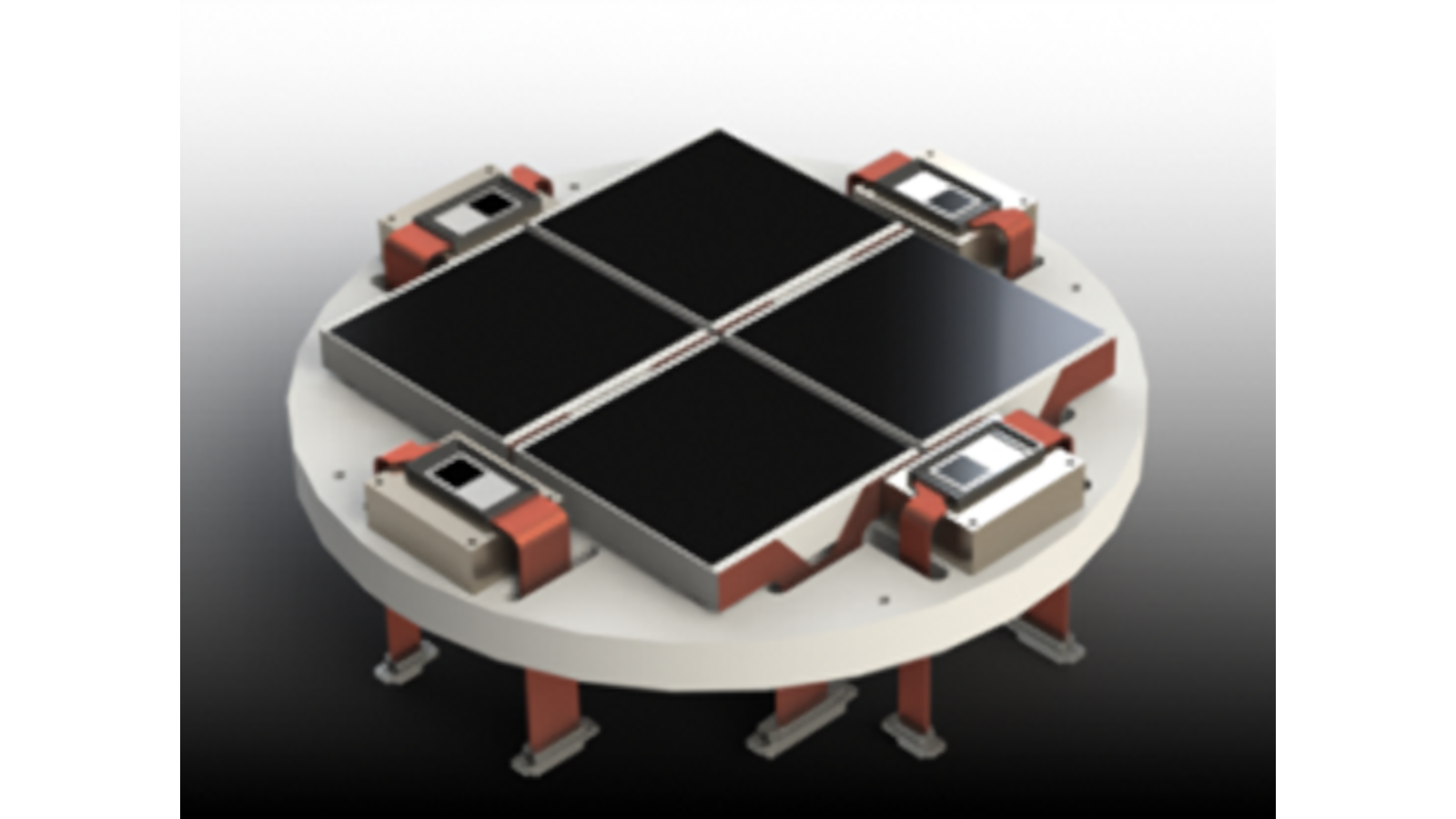
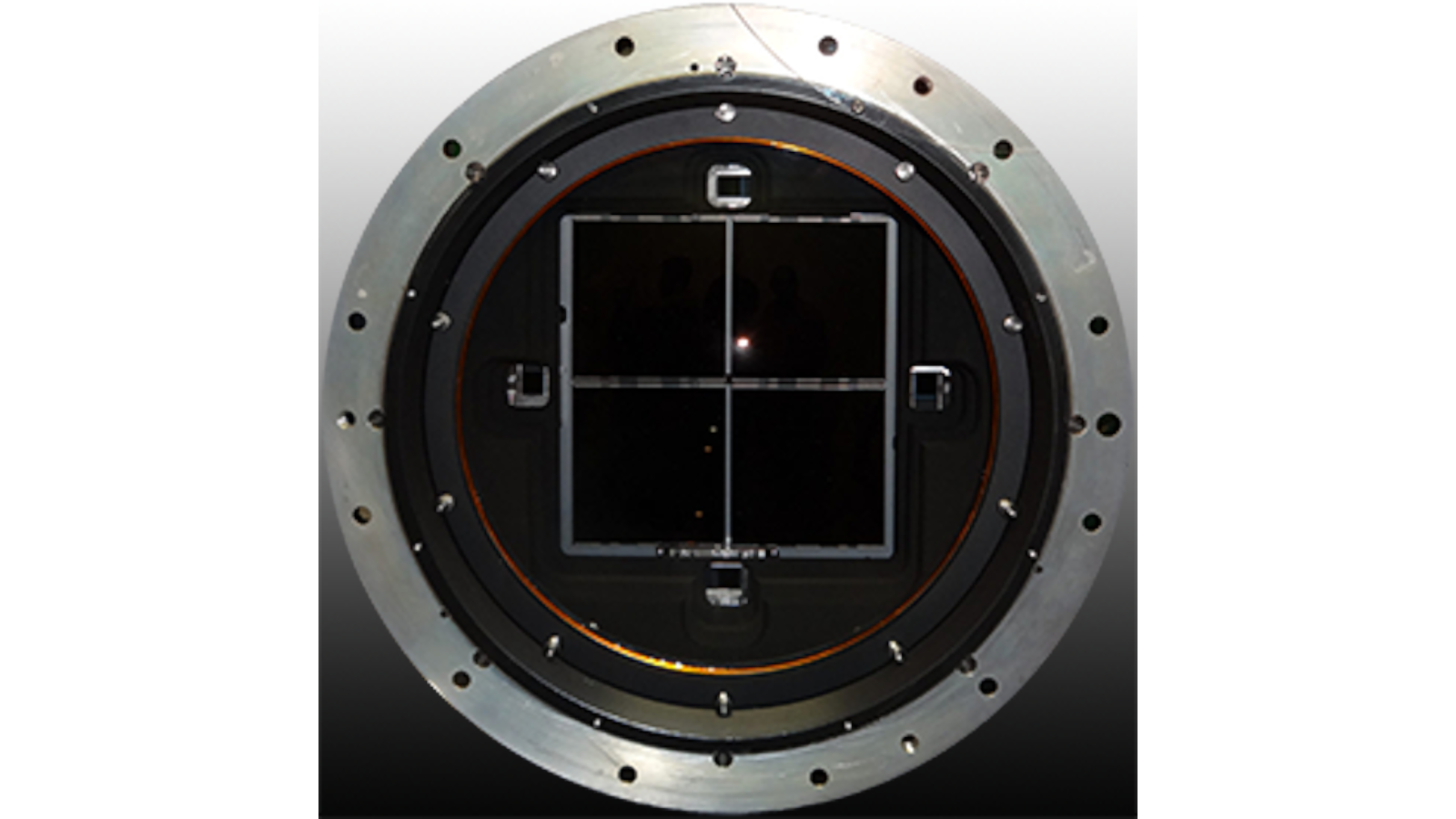
The Korean Microlensing Telescope Network (KMTNet) is comprised of three custom-built 1.6m telescopes with wide-field 340Mpixel CCD cameras designed and built by the ISL for the Korean Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI). The focal plane array is a mosaic of four (4) e2v CCD290-99 9Kx9K CCDs with a cryocooled dewar and readout electronics fabricated at OSU. The CCD mosaic gives a 2x2-degree field of view with optimal sampling for making images of the Galactic Bulge to identify exoplanets using the technique of gravitational microlensing.
The first KMTNet 18k Mosaic CCD camera was installed at Cerro Tololo in Chile in September 2014, the second at SAAO in South Africa in December 2014, and the third at Siding Springs Observatory in Australia in May 2015. They have been in continuous science operations since.
Instrument Specification
- Project type: Facility Instrument - wide field imagin camera
- Wavelength: 400-980nm
- Filters: Johnson-Cousins BVRI
- Field of View: 2x2-degrees
- Primary science: exoplanets (microlensing and transits), transients, solar system
- Telescopes: 1.6m KMTNet telescopes at CTIO, SAAO, and SSO
- Years active: 2014 - present
- Reference: Atwood et al., 2012, SPIE, 8446, 6GA
Instrument Facts
- Uses the largest CCDs made by E2V - 9Kx9K 10-micron CCD290-99 devices
- First ISL instrument to be completely cooled by closed-cycle cryocoolers instead of liquid nitrogen.
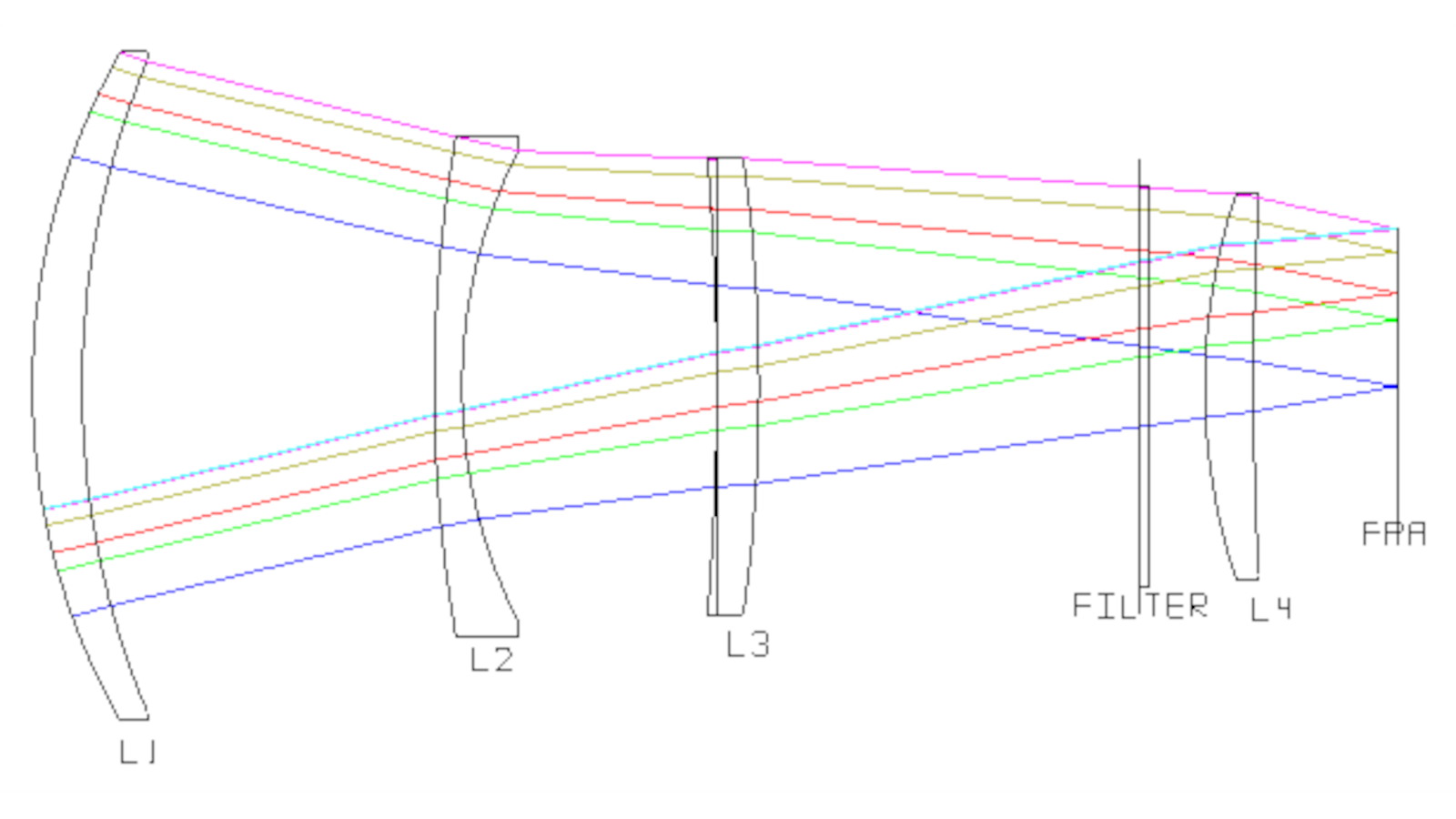
- The large front dewar window is the last lens in the custom prime-focus corrector lens of the telescope.
- Four frame-transfer CCDs located on the periphery of the focal plane are used for acquisition and guiding
- Readout time is 30 seconds with 32 readout channels.
- The KMT cameras are now the leading facility for the discovery of exoplanets by microlensing from the ground, and will only be surpassed with the launch of the Roman Space Telescope in the late 2020s.
Instrument Team
Bruce Atwood (PI)
Andrew Gould (Project Scientist)
Chung-Uk Lee (KASI lead)
Tom O'Brien (Senior Mechanical Engineer)
Mark Derwent (Mechanical Engineer)
Mark Johnson (Electrical Engineer)
Chris Colarosa (Engineering intern)
Jerry Mason (Software Systems Developers/Engineer)
Daniel Pappalardo (Electrical Engineer)
Skip Shaller (Software Engineer)